Command Line Interface
Introduction
Winter includes several command-line interface (CLI) commands and utilities that allow to install and manage Winter and its plugins and themes, perform site maintenance and speed up the development process. The console commands are executed through Laravel's Artisan command-line tool.
Commands are executed by using your terminal or shell and running the following command in the root folder of your project:
php artisan [command]
You can get a list of available commands by not providing any command to the Artisan tool:
php artisan
If you require help or a list of available arguments and options for each command, simply suffix the command with the --help flag:
php artisan [command] --help
Autocompletion / suggested input values
With the upgrade to Laravel 9 / Symfony 6, support was added for commands to be able to provide tab-autocomplete results to the shell for an improved user experience. Most Winter commands provide support for autocompletion of input values out of the box and it is easy to add support in your own custom commands when extending the Winter\Storm\Console\Command base class.
This feature requires that you run a command in your shell once in order to enable it for all Laravel / Winter console commands:
php artisan completion --help
Running just artisan completion will generate the shell script required to be imported into your shell in order to enable support for autocompletion of Winter / Laravel commands; passing the --help flag will provide detailed instructions on how to install the generated script.
List of available commands
The following commands are made available to every Winter installation. Click the name of a command to view more information about the usage of that command.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| Setup & Maintenance | |
winter:install |
Install Winter via command line. |
winter:update |
Update Winter and its plugins using the Marketplace via the command line. |
winter:up |
Run database migrations. |
winter:passwd |
Change the password of an administrator. |
winter:env |
Use environment files and configuration for Winter. |
winter:version |
Display the version of Winter in use. |
winter:fresh |
Remove the demo plugin and theme. |
winter:mirror |
Mirror publicly accessible files in another directory. |
| Plugin management | |
plugin:install |
Download and install a plugin for Winter. |
plugin:list |
List installed plugins. |
plugin:rollback |
Rolls back a plugin and its database tables. |
plugin:refresh |
Rolls back a plugin and its database tables, and re-runs all updates. |
plugin:disable |
Disables a plugin. |
plugin:enable |
Enables a plugin. |
plugin:remove |
Removes a plugin. |
| Theme management | |
theme:install |
Download and install a theme for Winter. |
theme:list |
List available themes. |
theme:use |
Switches Winter to the given theme. |
theme:remove |
Removes a theme. |
theme:sync |
Synchronises a theme between the filesystem and the database, if you use the Database Templates feature. |
| Asset compilation (Mix) | |
mix:install |
Install Node dependencies for registered Mix packages. |
mix:update |
Update Node dependencies for registered Mix packages. |
mix:list |
Lists all registered Mix packages. |
mix:compile |
Compiles one or more Mix packages. |
mix:watch |
Watches changes within a Mix package and automatically compiles the package on any change. |
mix:run |
Runs a script within a given package. |
| Scaffolding | |
create:command |
Create a Console Command class in a plugin. |
create:component |
Create a frontend Component in a plugin. |
create:controller |
Create a Controller in a plugin. |
create:formwidget |
Create a FormWidget in a plugin. |
create:job |
Create a Job class in a plugin. |
create:migration |
Create a Migration in a plugin. |
create:model |
Create a Model in a plugin. |
create:plugin |
Create a Plugin. |
create:reportwidget |
Create a ReportWidget in a plugin. |
create:settings |
Create a Settings model in a plugin. |
create:test |
Create a Test case in a plugin. |
create:theme |
Create a Theme. |
| Utilities | |
winter:test |
Run unit tests on Winter and plugins. |
winter:util |
A collection of utilities for Winter development. |
| Laravel Provided Commands | |
cache:clear |
Clear the application cache. |
cache:forget |
Remove an item from the cache |
clear-compiled |
Remove the compiled class file |
config:cache |
Create a cache file for faster configuration loading |
config:clear |
Remove the configuration cache file |
down |
Put the application into maintenance / demo mode |
event:cache |
Discover and cache the application's events and listeners |
event:clear |
Clear all cached events and listeners |
event:list |
List the application's events and listeners |
env |
Display the current framework environment |
key:generate |
Set the application key |
optimize |
Cache the framework bootstrap files |
package:discover |
Rebuild the cached package manifest |
queue:failed |
List all of the failed queue jobs |
queue:flush |
Flush all of the failed queue jobs |
queue:forget |
Delete a failed queue job |
queue:listen |
Listen to a given queue |
queue:monitor |
Monitor the size of the specified queues |
queue:prune-batches |
Prune stale entries from the batches database |
queue:prune-failed |
Prune stale entries from the failed jobs table |
queue:restart |
Restart queue worker daemons after their current job |
queue:retry |
Retry a failed queue job |
queue:retry-batch |
Retry the failed jobs for a batch |
queue:work |
Start processing jobs on the queue as a daemon |
route:cache |
Create a route cache file for faster route registration |
route:clear |
Remove the route cache file |
route:list |
List all registered routes |
schedule:finish |
Handle the completion of a scheduled command |
schedule:run |
Run the scheduled commands |
up |
Bring the application out of maintenance mode |
view:clear |
Clear all compiled view files |
Building a command
Plugins can also provide additional commands to augment additional functionality to Winter.
If you wanted to create a console command called myauthor:mycommand, you can run the php artisan create:command MyAuthor.MyPlugin MyCommand scaffolding command which would create the associated class for that command in a file called plugins/myauthor/myplugin/console/MyCommand.php with the following contents:
<?php namespace MyAuthor\MyPlugin\Console;
use Winter\Storm\Console\Command;
class MyCommand extends Command
{
/**
* @var string|null The default command name for lazy loading.
*/
protected static $defaultName = 'myauthor:mycommand';
/**
* @var string The name and signature of this command.
*/
protected $signature = 'myauthor:mycommand
{myArgument : Command argument avaible through $this->argument("myArgument")}
{--myOptionFlag : Defines a custom path to the "npm" binary}';
/**
* @var string The console command description.
*/
protected $description = 'Install Node.js dependencies required for mixed assets';
/**
* Execute the console command.
* @return int
*/
public function handle(): int
{
$this->output->writeln('Hello world!');
return 0; // return 1 if an error occurs
}
}
Once your class is created you should fill out the defaultName, signature, and description properties of the class, which will be used when displaying your command on the command list screen.
The handle method will be called when your command is executed. You may place any command logic in this method.
Defining input expectations
See the Laravel documentation for how to define the input expectations (arguments & options) that your command has.
Options for definining input:
- Input description
- Arguments
- Options
- Options with values
- Option shortcuts
- Input arrays
- Option arrays
- Input autocompletion / suggested values
- Plugin names as an argument
Providing suggested values
The Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\ProvidesAutocompletion trait provides a default implementation of the complete() method required to interact with the shell input autocompletion feature provided by Symfony. This simplifies the implementation work required in custom commands using an interface similar to the accessors in Eloquent.
NOTE: This trait is implemented by default in the
Winter\Storm\Console\Commandbase class.
In order to provide input suggestions for a given argument or option, all you have to do is add a method to your command class that is named in the following format: suggest{$inputName}[Values|Options](string $currentValue, array $currentInput): array.
Methods providing values for arguments should end in Values and methods providing values for options should end in Options. See below for a couple of example implementations:
// ...
/**
* Example implementation of a suggestion method for the "myArgument" argument
*/
public function suggestMyArgumentValues(string $value = null, array $allInput): array
{
if ($allInput['arguments']['dependent'] === 'matches') {
return ['some', 'suggested', 'values'];
}
return ['all', 'values'];
}
/**
* Example implementation of a suggestion method for the "package" option
*/
public function suggestPackageOptions(string $value = null, array $allInput): array
{
return Package::all()->pluck('name')->all();
}
// ...
See the Symfony documentation for more information.
Plugin names as an argument
If your command requires a plugin identifier as one of its arguments in order to scope the actions taken to that specific plugin, then you may use the System\Console\Traits\HasPluginArgument trait in order to provide automatic validation and normalization of the provided input as well as built in support for the input autocompletion feature.
Simply include the trait in your class and define plugin as an argument in your command's signature:
use Winter\Storm\Console\Command;
use System\Console\Traits\HasPluginArgument;
class MyCommand extends Command
{
use HasPluginArgument;
// ...
/**
* @var string The name and signature of this command.
*/
protected $signature = 'myauthor:mycommand
{plugin : The plugin to interact with. <info>(eg: Winter.Blog)</info>}';
// ...
/**
* @var string What type of plugins to suggest in the CLI autocompletion. Valid values: "enabled", "disabled", "all"
*/
protected $hasPluginsFilter = 'enabled';
public function handle()
{
// helper method that validates and normalizes the user provided input
$pluginName = $this->getPluginIdentifier();
// Do things with $pluginName
}
}
Retrieving input
See the Laravel documentation for how to retrieve input.
Available input methods:
- Retrieve input (arguments & options)
- Prompt for input
- Ask for confirmation (y/n)
- Ask for confirmation (required input string)
- Autocompletion / suggested answers
- Multiple choice questions
- Handling process signals
Confirmation via input
In addition to the extra input options that Laravel provides, the confirmsWithInput($message, $requiredInput) method can be used to display a warning message and a prompt that will ask the user to input the specified string in order to confirm a potentially destructive action.
This feature requires that your command includes the \Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\ConfirmsWithInput trait.
use Winter\Storm\Console\Command;
use Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\ConfirmsWithInput;
class MyCommand extends Command
{
use ConfirmsWithInput;
public function handle()
{
$pluginName = $this->argument('plugin');
if (!$this->confirmWithInput(
"This will remove the database tables and files for the \"$pluginName\" plugin.",
$pluginName
)) {
return 1;
}
// Do dangerous things with $pluginName
}
}
This will display the following:
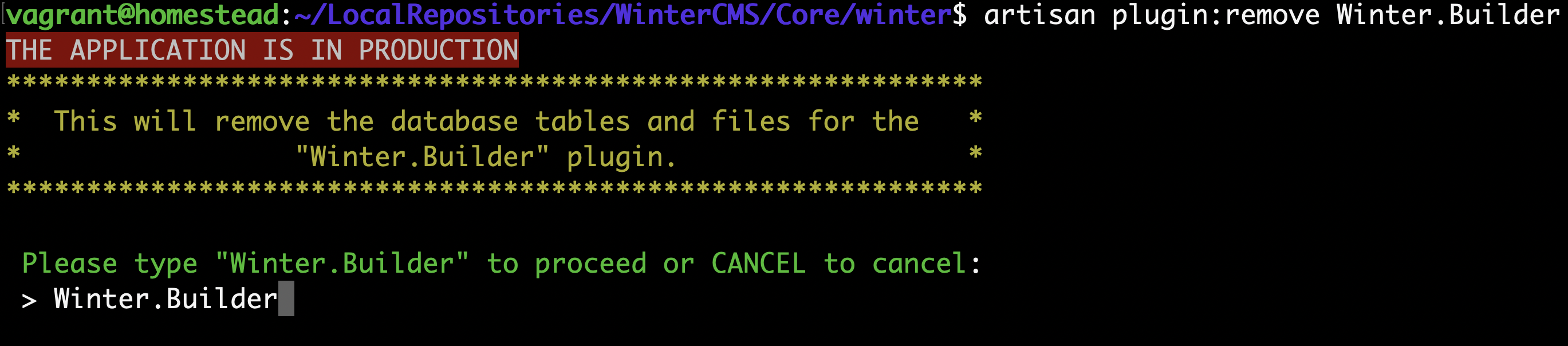
If your command defines a --force option in its signature, then that option can be used to bypass the confirmation step and production alert.
Handling process signals
The Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\HandlesCleanup trait provides a default implementation of the getSubscribedSignals() & handleSignal() methods required to interact with process signals forwarded by Symfony. This simplifies the implementation work required in custom commands for the common requirement of performing cleanup tasks when the command is terminated by the user in a cross-platform friendly manner.
NOTE: This trait is implemented by default in the
Winter\Storm\Console\Commandbase class. If you want to add it to a class that does not extend this base class you will also need to implement theSymfony\Component\Console\Command\SignalableCommandInterfaceinterface on your class.
To take advantage of this trait, either extend the base Winter\Storm\Console\Command class or add the Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\HandlesCleanup trait to your class and then implement the handleCleanup() method as shown below:
use Winter\Storm\Console\Command as BaseCommand;
class MyCommand extends BaseCommand // implements \Symfony\Component\Console\Command\SignalableCommandInterface
{
// Uncomment if not extending the BaseCommand class
// use \Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\HandlesCleanup;
// ...
/**
* Handle the cleanup of this command if a termination signal is received
*/
public function handleCleanup(): void
{
$this->newLine();
$workingPath = storage_path('tmp/my-working-file.json');
$this->info('Cleaning up: ' . $workingPath);
unlink($workingPath);
}
}
See the Symfony documentation for more information.
Processing Records
Winter provides the Winter\Storm\Console\ProcessesQuery trait for use in console commands that have to process a large number of records sourced from a database query. An example use of the trait is provided below:
<?php namespace MyAuthor\MyPlugin\Console;
use Winter\Storm\Console\Command;
use MyAuthor\MyPlugin\Models\MyModel;
class ProcessRecords extends Command
{
use \Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\ProcessesQuery;
use \Winter\Storm\Console\Traits\ConfirmsWithInput;
/**
* @var string The console command name.
*/
protected static $defaultName = 'myplugin:processrecords';
/**
* @var string The name and signature of this command.
*/
protected $signature = 'myplugin:processrecords
{--limit=0 : The maximum number of records to process. Defaults to all.}
{--chunk=100 : The number of records to process at once.}
{--f|force : Force the operation to run and ignore production warnings and confirmation questions.}
';
/**
* @var string The console command description.
*/
protected $description = 'Processes the selected records';
/**
* Execute the console command.
*/
public function handle(): int
{
// Build the query that will retrieve all the records to be processed
$query = MyModel::query()->withTrashed();
// Get the total number of records to be processed for the alert message
$totalRecords = $query->count();
// Ask the user to confirm the processing action by entering the number
// of records to be affected
if (!$this->confirmWithInput(
sprintf(
'This will process all selected records, a total of %s.',
number_format($totalRecords)
),
$totalRecords
)) {
return 1;
}
// Process the records
$this->processQuery(
$query,
function ($record) {
$record->myCustomAction();
},
$this->option('chunk'),
$this->option('limit')
);
return 0;
}
}
Writing output
See the Laravel documentation for how to send output to the console.
Available output methods:
- Information message (green text)
- Error message (red text)
- Plain text
- New Lines
- Tables
- Progress Bars
- Alerts
Alerts
The alert($message) method makes it easy to render an "alert box" with the provided message in order to draw more attention to an important notice.
This method is also provided by Laravel (currently undocumented), however Winter's implementation also includes support for automatically wrapping the alert box size to the standard 80 characters of width to prevent long messages from breaking the formatting of the alert box.
$this->alert('This will remove the database tables and files for the "Winter.Builder" plugin.');
Will output
*************************************************************
* This will remove the database tables and files for the *
* "Winter.Builder" plugin. *
*************************************************************
Registering commands
Registering a console command
Once your command class is finished, you need to register it so it will be available for use. This is typically done in the register method of a Plugin registration file using the registerConsoleCommand helper method.
class MyPlugin extends PluginBase
{
public function register()
{
$this->registerConsoleCommand('myauthor.mycommand', \MyAuthor\MyPlugin\Console\MyCommand::class);
}
}
Alternatively, plugins can supply a file named init.php in the plugin directory that you can use to place command registration logic. Within this file, you could use the Artisan::add method to register the command:
Artisan::add(new MyAuthor\MyPlugin\Console\MyCommand);
Registering a command in the application container
If your command is registered in the application container, you may use the Artisan::resolve method to make it available to Artisan:
Artisan::resolve('myauthor.mycommand');
Registering commands in a service provider
If you need to register commands from within a service provider, you should call the commands method from the provider's boot method, passing the container binding for the command:
public function boot()
{
$this->app->singleton('myauthor.mycommand', function () {
return new \MyAuthor\MyCommand\Console\MyCommand;
});
$this->commands('myauthor.mycommand');
}
Calling other commands
See the Laravel documentation for how to call commands programmatically.